A SWIR (Short-Wave Infrared) vision system consists of several components that work together to capture, process, and analyze images in the SWIR spectrum. Here is a detailed description of each component:
1. SWIR Camera
- Sensor: InGaAs Sensor: The most common sensor type for SWIR cameras is made of indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs), which is highly sensitive to the SWIR wavelength range (approximately 0.9 to 1.7 microns). InGaAs sensors are favored for their high quantum efficiency and low noise characteristics in the SWIR range (check out our blog What Is InGaAs? for more information.)
- Resolution: SWIR cameras come with various resolutions, from low-resolution sensors for basic applications (typically QVGA resolution with 0.3MP resolution) to high-resolution sensors (up to 5.3 MP with the new Sony IMX992) for detailed imaging and analysis.
- Frame Rate: The frame rate of a SWIR camera can vary depending on the application, with some cameras capable of high-speed imaging for dynamic scenes. (Check out our blog post about High-Speed SWIR Imaging for more information.)
- Cooling System: Some SWIR cameras feature cooling systems (such as thermoelectric coolers) to reduce thermal noise, enhancing image quality, especially in long-exposure applications. (Check out our blog To Cool Or Not To Cool for more information.)

2. SWIR Lenses
SWIR-Specific Lenses: Lenses designed specifically for SWIR wavelengths ensure optimal transmission and focus across the SWIR range. Different types of lenses can be used in a SWIR vision system depending on the application:
- Fixed focal length lenses provide a fixed field of view. The field of view is calculated using the sensor size and focal length of the lens.
- Telecentric lenses are used for precision optical two-dimensional measurements and other applications that are sensitive to the image magnification or the angle of incidence of light.
- Microscope objective lenses are used for high magnification imaging at microscopic scales.
- Zoom lenses are typically motorized and used for long range surveillance. They often include motorized iris and focus controls.

3. SWIR Illumination
- SWIR LEDs: Emit light in the SWIR range to illuminate the target scene, particularly useful in low-light conditions or for enhancing contrast. Typical SWIR LED illuminations consist of a LED ring, LED bar or backlight.
- SWIR Lasers: Provide coherent light in the SWIR spectrum, often used for applications requiring precise illumination or long-distance imaging.
- Halogen lamps: Provide broadband illumination at the expense of high heat generated, which can impact samples and/or measurements.

4. Optics
- Optical Filters: Filters are used to selectively transmit or block certain wavelengths within the SWIR range, enhancing contrast and reducing spectral noise. This can be crucial for isolating specific features or materials in the scene.
- Beam Splitters: Used in some systems to direct SWIR light to multiple detectors or optical paths, allowing simultaneous multi-spectral imaging or analysis.
5. Image Acquisition System
- Frame Grabber: A hardware component that captures the video signal from the SWIR camera and converts it into a digital format suitable for processing and analysis.
- Data Interface: Interfaces like USB, GigE, Camera Link, or CoaXPress facilitate the transfer of image data from the camera to a computer or processing unit.
6. Image Processing & Analysis Software
- Image Processing Algorithms: Software tools that process raw SWIR images, including functions like noise reduction, contrast enhancement, and feature extraction to prepare images for analysis.
- Analysis Tools: Applications for analyzing processed images, performing tasks such as defect detection, material identification, and quantitative measurements.
- Machine Learning: Advanced systems may integrate machine learning algorithms for automated analysis, pattern recognition, and decision-making based on SWIR images.
7. Control System
- Camera Control Software:Software to adjust camera settings, such as exposure time, gain, and frame rate, to optimize image capture based on specific conditions and requirements.
- Synchronization:Systems that synchronize the camera with other components, such as lighting sources or external triggers, to coordinate image capture with other events or processes.
Example of a SWIR Vision System
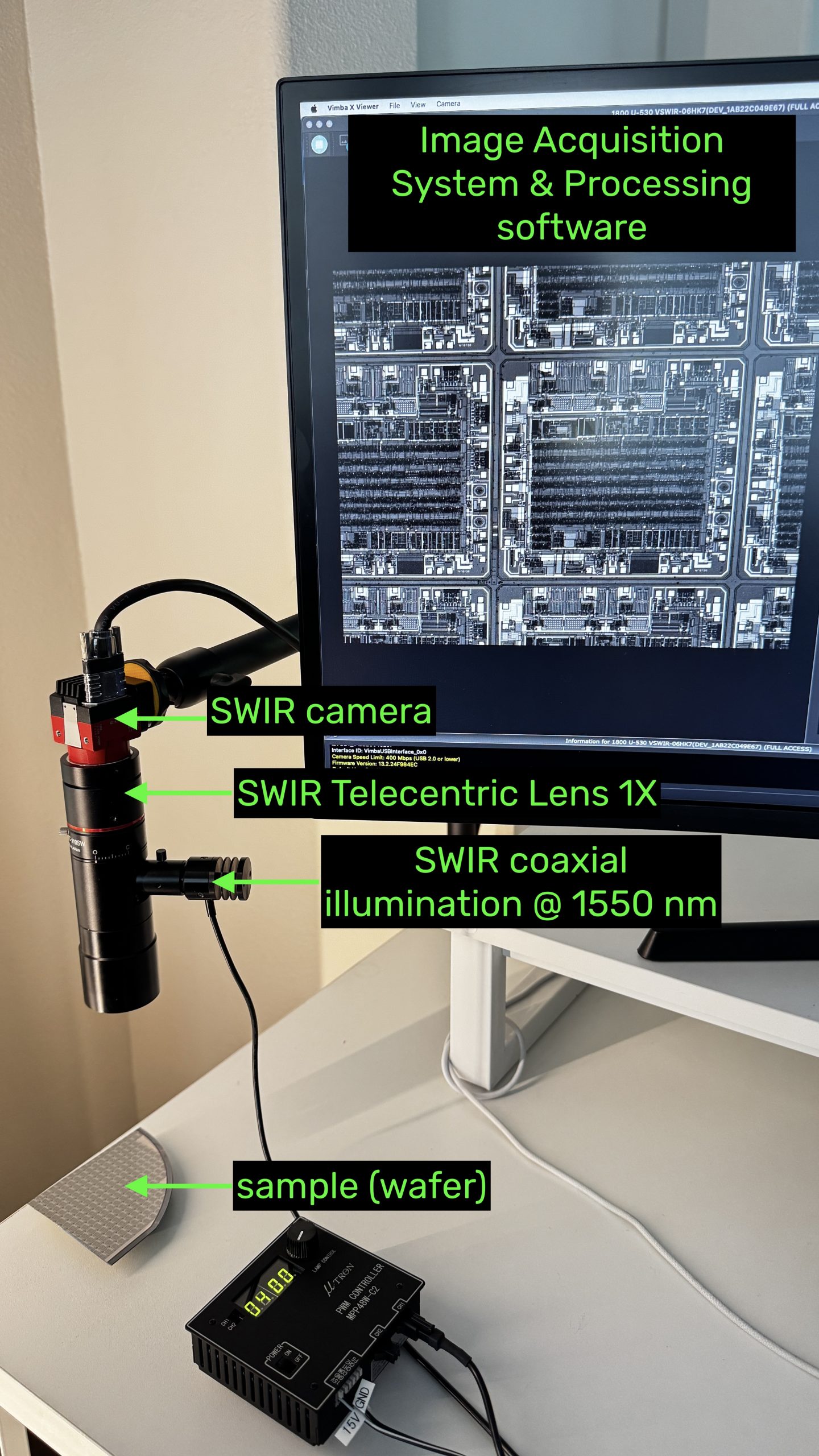

SWIR Camera: Alvium U-530 SWIR camera with 5.3 MP resolution and 3.45 µm pixel pitch
SWIR Lens: telecentric lens 1x with coax port
SWIR Illumination: LED spotlight at 1550 nm for coaxial port
Optics: long-pass filter > 920 nm to cut-off visible wavelengths (optional here as LED source is single wavelength)
Image Acquisition system: USB video interface to computer + VIMBA X
Image Processing: VIMBA X Viewer
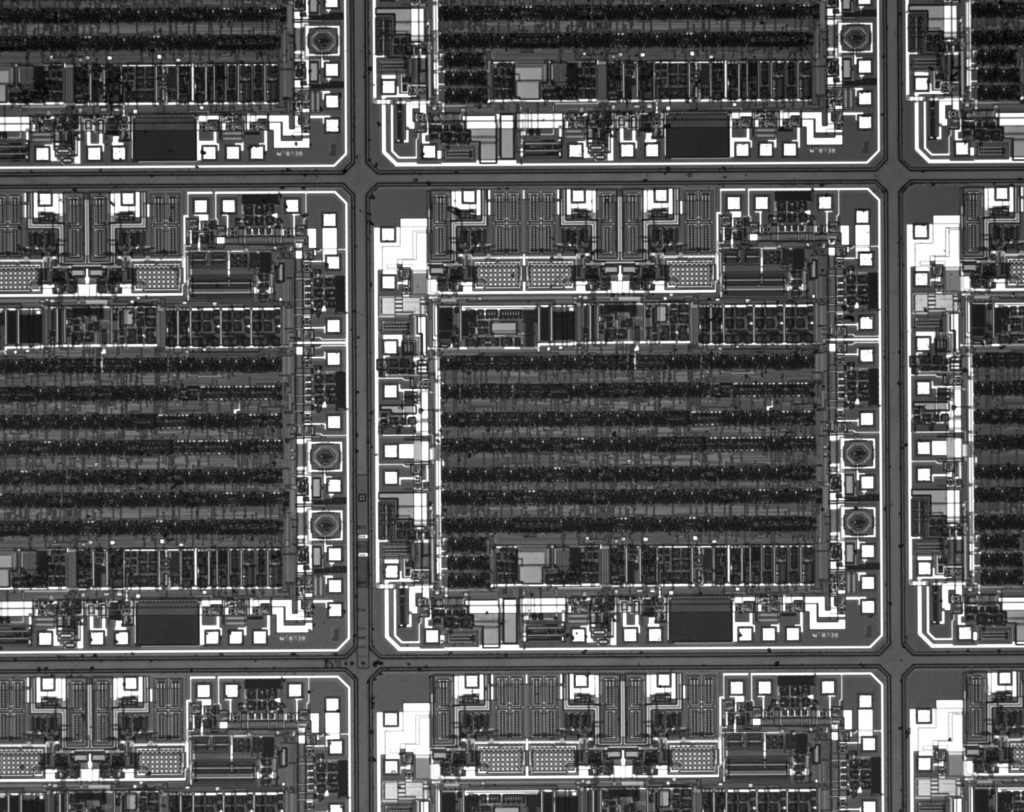
Si wafer as seen by Alvium U-530 with IMX992 and 1X telecentric lens